
Blog
Four ways to boost CX with seamless transactions

Event
Genesys APAC Partner Conference, Bangkok, Thailand

Event
Genesys Xperience, Denver, CO

Event
Enterprise Connect, Orlando, FL

Blog
Three steps to taking the complexity out of contact center payments

News
PCI Pal® is Awarded Payments Compliance Technology of the Year at Payments Awards 2023

News
PCI Pal Teams up with Zoom to Create Exceptional Secure Payment Experiences

News
PCI Pal Named 2023 Compliance Software Solution of the Year

Blog
Secure Payment Solution Providers: Key to Call Center Security

Blog
AI-Powered Speech Recognition Payments: A Strategy for Contact Centers

News
PCI Pal Augments Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) Solution

News
Golden Nugget partners with PCI Pal® to Improve Payment Experience with Conversational AI

Video
Golden Nugget Case Study

Success Story
Enhancing contact center payment security and compliance for Secret Escapes

News
PCI Pal® supports Secret Escapes in enhancing Payment Card Security and Compliance

News
PCI Pal Extends Partnership with PCI Security Standards Council to Help Secure Payment Data Worldwide

News
PCI Pal receives triple shortlisting at the 2023 Payments Awards

Blog
Driving a Successful Customer Journey: The Contact Center Agent Experience

Success Story
Crafting Trust: Arts & Crafts Superstore Protects Customer Payments

News
PCI Pal Achieves AWS Service Ready Designation for Amazon Connect

Blog
Could enhancing your contact centre customer experience be the key to unlocking customer loyalty?

Blog
PCI DSS Compliance Checklist

Blog
Conversational AI: Payment Fraud Prevention and Data Protection

News
PCI Pal is Enhancing Contact Center Payments Through the Power of Conversational AI

Podcast
Securing Contact Centers: Beyond Pause and Resume Recording

Blog
Protecting Online Card Payments: Explore PSD2 and 3D Secure

News
PCI Security Standards Council welcomes PCI Pal® CISO, Geoff Forsyth, to its Board of Advisors

Blog
Exploring ACH and Open Banking: US vs. Europe

News
PCI Pal Named Finalist in 2023 Security Awards

White Paper
Pause and Resume Call Recording: Calculating the Risk

News
PCI Pal® listed in Growth Index Top 100 ranking of UK’s fastest growing companies for the second consecutive year

News
NFP Health Deploys PCI Pal to Streamline Contact Center Payments

Success Story
NFP Health Secures Remote Contact Center Payments with PCI Pal

Blog
Securing ACH Payments in Contact Centers

News
PCI Pal Featured on CardRates.com

Blog
Why Pause and Resume Call Recording Isn’t Enough

Blog
4 Steps to Secure Contact Center Payments

Blog
A Guide to Digital Payment Link Security

Success Story
Darlington Borough Council

News
Darlington Borough Council Secures Contact Center Payments with PCI Pal®

Podcast
Payments Trends and Predictions for 2023

Infographic
Preparing for the ADPPA

Blog
How Businesses Can Prepare for the ADPPA

Infographic
Five Key Factors Influencing Consumer Payment Preferences

News
GoSee Enhances Contact Center Payment Experience with PCI Pal

Blog
What are the main differences and similarities between PCI DSS and HIPAA?

Blog
Consumer Benefits of Pay by Bank

News
PCI Pal Shares Top Predictions for Payment and Security Trends in 2023
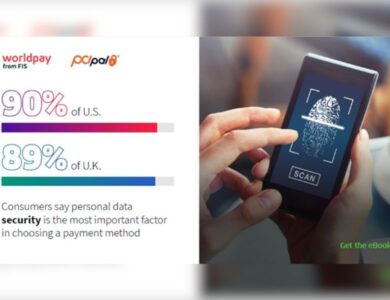
News
Future of Payments survey finds increasing consumer trust toward digital payment methods

News
PCI Pal’s New Pay By Bank Innovation Shortlisted for 2023 Card & Payments Awards

News
PCI Pal extends G-Cloud certification

Blog
Security risk: Are you still using POS terminals in your contact center?

News
Air Europa chooses PCI Pal Agent Assist to enhance Contact Center payment processes

Success Story
Air Europa futureproofs payment security and CX with PCI Pal

Blog
Contact centers are shifting gears: Entering the era of digital payments

News
PCI Pal Named “Data Security Solution Provider of the Year” in 2022 CyberSecurity Breakthrough Awards Program

News
PCI Pal Partners with Virgin Atlantic to Secure its International Omnichannel Payments

News
Cybernews Payments Interview with PCI Pal’s CISO

News
PCI Pal Launches Open Banking Payments for Contact Centers: the first in a series of new payment products

Podcast
Keep Calm and Simplify

News
PCI Pal Extends Patent Portfolio in US and Australia for Processing Sensitive Information over VoIP

Success Story
National Express boosts customer service with 8×8 and PCI Pal

Podcast
Payments 22: The Future of Security and CX

Blog
Simplifying Contact Center Payment Security

News
Teleperformance UK selects PCI Pal to secure expanding payment methods for global enterprise customers

News
PCI Pal Named Winner in Coveted Categories at Annual CNP Awards and Global Infosec Awards
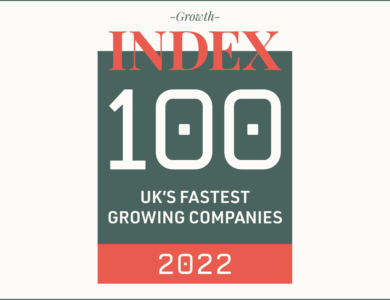
News
PCI Pal ranked in the top 100 Fastest growing companies in the UK

Video
Calabrio Presents: Improving Customer Experiences through Performance Management

News
Freshworks and PCI Pal partner to futureproof omnichannel payment security for Bensons for Beds

Success Story
Bensons for Beds futureproofs omnichannel payment security with PCI Pal and Freshworks

Podcast
PCI DSS v4.0: What it means for Compliance in the Cloud

Ebook
Starting Your PCI Compliance Journey

Infographic
Data Privacy in Australia

News
PCI Pal, Servadus, and Verizon Release Joint White Paper Addressing Contact Center Best Practices in the Wake of PCI DSS 4.0 Rollout

White Paper
Keep Calm and Simplify: Contact Center Best Practices in the Era of PCI DSS 4.0

Video
Talkdesk Presents: Delivering Better Payment CX

Ebook
This is Australia 2022: The State of Security through the Eyes of Australian Consumers Today

Video
Worldpay from FIS Presents: Digitizing B2B Payments

Infographic
Data Privacy Legislation and Payments in Canada

News
PCI Pal partners with Odigo to provide secure payments

Success Story
Greg Rowe Limited partners with Talkdesk and PCI Pal for secure payments

News
Greg Rowe’s contact center solution keeps customer communications and payments flowing with technology from Talkdesk and PCI Pal

Blog
PCI DSS v4.0 and Payment Security: What You Need to Know

News
PCI Pal partners with Five9 to provide secure payments on the Five9 CX Marketplace

Success Story
Public Sector – PCI Compliance for Australian Government Authority

News
Restaurant group Fridays UK chooses PCI Pal® to secure card payments

Success Story
Retail – PCI Compliant Payments for Restaurant Group Fridays

News
PCI Pal® unveiled as 21st best-performing tech scale-up in the UK at 2022 Megabuyte Emerging Stars awards

News
Survey Finds All Payment Channels Face a Distrust Deficit in the Wake of COVID-19

Ebook
This is Canada 2022: The State of Security through the Eyes of Canadian Consumers Today

News
PCI Pal® marks Australian launch with senior VP appointment

Success Story
Retail – Major British Multinational Retailer

News
PCI Pal® wins Best Compliance Product at the CX Awards 2022

News
PCI Pal® announces new global partnership with VoiceFoundry, a TTEC Digital Company.

Podcast
Love your customer

Success Story
Utilities – PCI Compliant Contact Center Payments for Natural Gas Supplier

News
The Call & Contact Center Expo Names PCI Pal Finalist for Security Solution of the Year

News
PCI Pal® shortlisted for the Best Compliance Product in the CX Awards 2022

Success Story
Retail – Secure Payments for Leading European Furniture Manufacturer

Success Story
BPO – Securing Payments for Leading US Business Process Outsourcer

News
International Survey Probes the Future of Customer Service and Considers Consumer Preferences versus Contact Center Strategies

Ebook
Security in the Contact Center: A Comparative Study of Consumers and Contact Center Professionals

News
PCI Pal Provides Secure, Compliant Payments for Talkdesk Global Customers

News
Delivery speed and transaction security top the list of festive shoppers’ worries for 2021, in PCI Pal®’s annual yuletide survey

Success Story
Secure phone payments for leading US cable provider

Podcast
Working smarter – are you PCI compliant?

News
PCI Pal® finalists in 2022 Card and Payments Awards

News
Chill Out, Relax, Take It Easy: PCI Pal® Removes the PCI Compliance Worry from Chill Insurance

Success Story
PCI Compliant Payments for Chill Insurance

News
Gearing up for 2022: PCI Pal® Releases Top-Level Insights to Prepare Businesses for a New Year of Cyber Crime

News
Michelin implements PCI Pal® for Secure and Compliant Payments

Success Story
Retail – PCI Compliance for a Global Appliance Manufacturer

News
PCI Pal® wins Payments Compliance Technology of the Year at the Payments Awards 2021

News
PCI Pal® wins Payment Solution award at the Credit & Collections Technology Awards

News
PCI Pal® wins three accolades at the WorkL Workplace of the Year Awards

Success Story
Retail – Secure Omnichannel Contact Center Payments

News
Puzzel extends partnership with PCI Pal®’s omnichannel payment portfolio

News
PCI Pal® to discuss The Future of Security & CX at Call and Contact Centre Expo 2021

News
Happiness matters: PCI Pal® shortlisted for WorkL Workplace of the Year Awards 2021, supported by The Telegraph

Video
What Is PCI Compliance?

News
PCI Pal® shortlisted for Enterprise Security Solution award at Security Excellence Awards 2021

News
PCI Pal Announces Amazon Connect Integration and AWS Marketplace Availability

News
Cybersecurity breach at Neiman Marcus will test consumers’ retail confidence ahead of the busy festive period, warns PCI Pal

Ebook
Securing Payments in an Omnichannel Contact Center

News
PCI Pal® and Puzzel secure telephone payments for GC Business Finance

Success Story
Financial – GC Business Finance

News
PCI Pal® signed-up to reduce payment security risk for Essex County Council

News
Fewer than 10% of People are Confident about their Data Security on Social Media, According to Survey from PCI Pal

News
PCI Pal® announced as a finalist in the 2021 Cloud Excellence Awards

Podcast
Securing Payments in 2021 Australia

Infographic
Descoping: An Investment Providing Savings & Returns

Ebook
A Security Assessor’s Guide

News
PCI Pal® Publishes Payments: The Future of Security and CX Whitepaper

White Paper
Payments: The Future of Security & CX

News
PCI Pal® and Their Partner 8×8 to Discuss Reimagining Service Delivery at the SOCITM President’s Week 2021

News
PCI Pal® Solutions Now Available as a Premium App on Genesys AppFoundry

News
InsureandGo Extends PCI Pal® Payment Security Solution to Australian Operations

Podcast
PCI DSS v4.0: The Challenges for Organizations and QSA’s

News
PCI Pal® Awarded Best Call Centre Solution at CNP 2021

News
Halfords Places Customer Service and Experience in Pole Position

Infographic
Which Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) Is Right for You?

Success Story
Retail – Halfords

News
AvalonBay Selects PCI Pal® to Securely Handle its Contact Center Payments

Success Story
Leisure – AvalonBay

Podcast
Post Pandemic Payments

News
PCI Pal® Appoints Mufti Monim as New CTO

Podcast
Payments: The Future of Compliance and CX

News
PCI Pal® Supports Royal Exchange Theatre With Its Payment Security Compliance

Video
Ciske van Oosten Presents Payments 2021 Closing Keynote: Engineering Effective & Sustainable Payment Security by Design

Video
Neira Jones Presents Payments 2021 Opening Keynote: Secure Payments, CX Friend or Foe?

News
PCI Pal® Releases Podcast Highlighting the Top 5 Agenda Items for CISOs in 2021

Podcast
Podcast: Five Agenda Items for CISOs in 2021

News
PCI Pal® Encourages Organizations to Consider Adopting a Company Culture of Security and Compliance on Data Protection Day 2021

News
PCI Pal® Announces Partners for Upcoming Payments: The Future of Security and CX Conference

Podcast
Podcast: Making Compliance a Habit

News
Online Shoppers More Concerned About Deliveries Than Personal Security, According to PCI Pal® Survey

Podcast
Podcast: Compliance in the Cloud

Podcast
Podcast: Compliance for the Public Sector

News
Predicting the Unpredictable: PCI Pal Releases Cybersecurity and Compliance Predictions for 2021

News
PCI Pal® Supports InsureandGo with Payment Security and Compliance

News
PCI Pal® Shortlisted for Best Technology Initiative at the Card and Payments Awards

Success Story
Financial – MAPFRE: InsureandGo

Success Story
Government – South Staffordshire District Council

Video
Agent Assist Solution

Video
IVR Solution

Infographic
PCI DSS Compliance Comes Under the Spotlight in Verizon’s 2020 Payment Security Report

Ebook
Partner Program Datasheet

Success Story
Retail – TRADER

News
PCI Pal® Receives G-Cloud 12 Certification

Webinar
What Now? Future-Proofing Your Payments

News
PCI Pal Announces Partnership with Calabrio and Joins the Calabrio Marketplace

News
PCI Pal® Recognized as Notable Tech Innovator Following Tech East 100 Award

Ebook
Solutions Brochure

Success Story
Logistics – Logistics Industry Success Story

News
PCI Pal® Adds Speech Recognition Capability to Its Cloud-Based Agent Assist and IVR Payment Solutions

News
PCI Pal® Announces the Formation of the PCI Pal Advisory Committee and Its First Member, Neira Jones.

News
PCI Pal® SVP Nominated in the Computing Women in Tech Excellence Awards

News
PCI Pal® Announced as Finalist in Insurance Times Tech & Innovation Awards

News
PCI Pal® and Civica Host Payments Security and Compliance Webinar for the Public Sector

News
Survey Finds Majority of Europeans Will Take Custom and Loyalty Elsewhere Following a Security Breach

News
Survey From PCI Pal® Reveals Australians’ Concerns Relating to Data and Payment Security Practices During the Coronavirus Pandemic

News
PCI Pal Partners With Avaya Contact Center to Deliver an Integrated Cloud-Based Compliance Solution for Telephone and Digital Payments

News
PCI Pal® Progresses Partnership with Leading Cloud Contact Center Provider Talkdesk
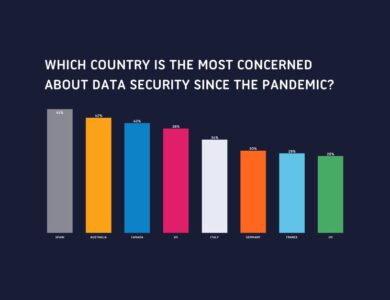
Infographic
Data Security in the Eyes of the Consumer Post COVID-19

News
Waltham Forest Council Implements PCI Pal to Secure Cardholder-Not-Present Payment Transactions

News
Survey From PCI Pal® Shows Significant Consequences for Businesses that Demonstrate Poor Data Security Practices During the Pandemic

Success Story
Government – Waltham Forest

News
Pennon Water Services Keeps Its Customer Experience Flowing Thanks to Vonage and PCI Pal®

Success Story
Utilities – Pennon Water Services

Success Story
Public Sector – Delivering Security and Compliance to the Public Sector

News
PCI Pal® Shortlisted for Omnichannel Solution of the Year

News
PCI Pal® Launches Webinar Series on Payment Security Compliance

News
PCI Pal® Launches New Capability to Rapidly Deliver Secure Payment Services to Businesses With Home and Remote Workers Within 48 Hours

Infographic
PCI Compliance: Then & Now

Infographic
PCI Compliance for Large Organizations: 10 Tips

News
PCI Pal Nominated for Best Compliance Provider Award at CNP 2020

Video
SixPackAbs Case Study
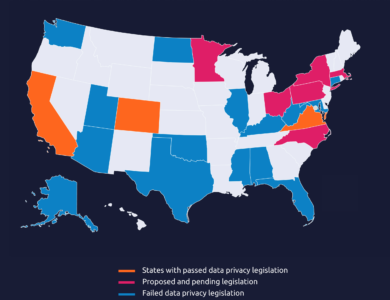
Infographic
Data Privacy in the US

News
PCI Pal® Launches PCI Pal Digital for Omnichannel Payment Security

News
PCI Pal® Wins PCI Excellence Award in Recognition of Customer Success

News
PCI Pal® Advances to a Cisco Preferred Solution Partner

News
Vax Transforms Telephone Payment Transaction Process With PCI Pal®

Success Story
Retail – VAX

Success Story
Government – Delivering Compliance to Local Authorities

Webinar
Compliance in the Cloud

News
PCI Pal® Selected for Membership in Avaya’s DevConnect Program

News
PCI Pal® Study Reveals That Londoners Are the Biggest Risk Takers With Their Personal Data Security Practices

Video
PCI Pal Digital

News
PCI Pal® Urges Businesses to Remove ‘Tick Box’ Mentality to Ensure Year-Round PCI DSS Compliance

News
PCI Pal® Receives Double-Shortlisting in the 2020 Card and Payment Awards

News
Woodland Trust Enhances Telephone Payment Security With PCI Pal

News
The Woodland Trust Enhances Telephone Payment Security Thanks to PCI Pal®

Success Story
Healthcare – British Medical Journal

Success Story
Financial – Verex

News
PCI Pal® Builds on UK Partnership With 8×8 to Offer Secure Payment Services for Contact Centers Globally

News
PCI Pal Named “Compliance Software Solution Provider of the Year” Award in 2019 CyberSecurity Breakthrough Award Program

News
PCI Pal® Announced as EMEA AppFoundry Partner of the Year at Genesys’ G-Summit Europe

News
PCI Pal® Shortlisted for Further Industry Awards

News
Inadequate Data Security Practices Come With Serious Financial Consequences for Canadian Businesses

Success Story
Utilities – Ecotricity

Ebook
This is Canada: The State of Security in the Eyes of Canadian Consumers 2019

Ebook
This is Australia: The State of Security in the Eyes of Australian Consumers 2019

Success Story
Retail – Six Pack Abs

News
PCI Pal® and Verizon White Paper Examines PCI Security Compliance in Contact Center Environments

White Paper
Keep Calm and Descope

Success Story
Outsourcing – DDC Outsourcing Solutions UK

Video
Agent Assist – Agent Demo

News
PCI Pal® Wins At CNP 2018 Awards

News
PCI Pal® Shortlisted for Comms Business Awards 2018

Success Story
Leisure – iFLY Indoor Skydiving

News
PCI Pal® Shortlisted for Retail Security Initiative of the Year at the Retail Systems Awards 2018

News
PCI Pal® Announced as Cisco Solution Partner for EMEA, USA & Canada

Video
Agent Assist – How it Works

News
PCI Pal® To Attend Call & Contact Expo 2018

News
8×8 and PCI Pal Partner on Compliance

News
PCI DSS 3.2 Set to Expose ‘Compliance Cramming’ Culture, Warns PCI Pal®

News
PCI Pal® Celebrates an Award Win at the PCI 2018 Awards for Excellence

News
PCI Pal® Shortlisted for the 2018 Card and Payments Awards

Success Story
Retail – AllSaints

Video
AllSaints Case Study

Success Story
Outsourcing – Serco

Success Story
Leisure – KidZania

Video
Serco Case Study

Video
Kidzania Case Study

Video

